Spaghetti Model Fundamentals: Hurricane Beryl Spaghetti Models
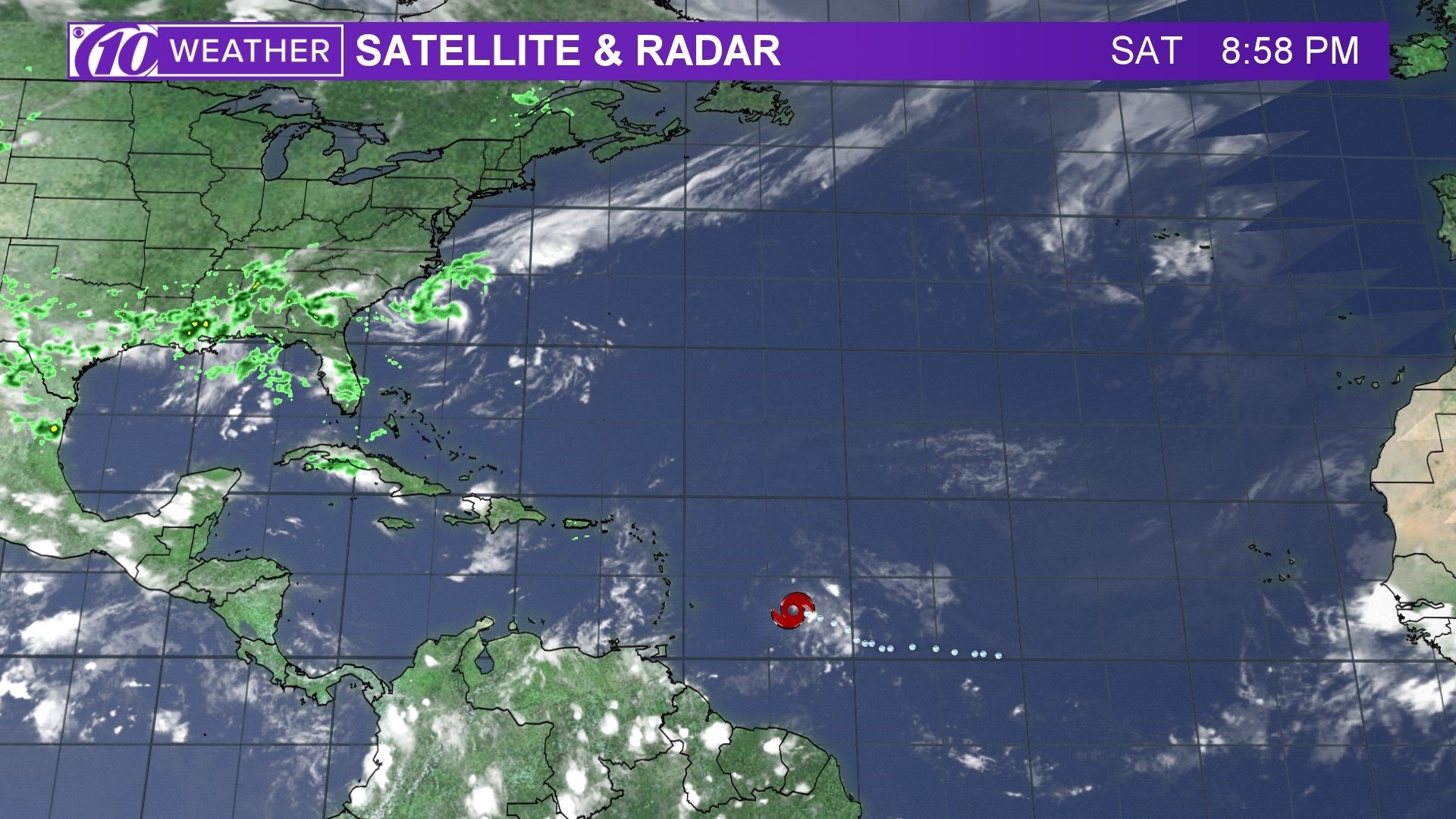
Hurricane beryl spaghetti models – Spaghetti models, also known as ensemble forecast models, are a collection of computer model runs that provide a probabilistic forecast of a hurricane’s track and intensity. Each model run uses slightly different initial conditions and model physics, resulting in a range of possible outcomes. By examining the spread of these outcomes, forecasters can assess the uncertainty in the forecast and make more informed decisions.
Hurricane Beryl spaghetti models give us an idea of the possible paths the storm could take. To get a more accurate prediction, we can check hurricane beryl prediction. This can help us better prepare for the storm’s impact. By following the spaghetti models and checking predictions, we can stay informed and make the necessary arrangements to stay safe.
Key Features
- Ensemble Members: Spaghetti models consist of multiple individual model runs, each representing a possible evolution of the hurricane.
- Probabilistic Forecast: By analyzing the distribution of model outcomes, spaghetti models provide a probabilistic forecast, indicating the likelihood of different outcomes.
- Uncertainty Visualization: The spread of the model runs graphically depicts the uncertainty associated with the forecast.
Limitations
- Model Errors: Spaghetti models are still subject to model errors and uncertainties, which can impact the accuracy of the forecast.
- Computational Cost: Running multiple model simulations is computationally expensive, limiting the frequency and resolution of spaghetti model forecasts.
- Interpretation Challenges: Interpreting spaghetti models can be challenging, especially for non-experts.
Example
Consider a spaghetti model that shows a range of possible tracks for Hurricane Beryl. The model runs indicate that the hurricane could make landfall anywhere from Florida to North Carolina. The spread of the model runs suggests that there is uncertainty in the forecast track, and the exact location of landfall is not yet known. Forecasters will continue to monitor the spaghetti model and other forecast tools to refine the forecast as the hurricane approaches.
Hurricane Beryl spaghetti models show a range of possible tracks, some of which could bring the storm near Puerto Rico. The island is still recovering from the devastation caused by Hurricane Maria in 2017, and another hurricane would be a major setback.
Residents are urged to monitor the storm’s progress and be prepared to take action if necessary.
Beryl’s Spaghetti Model Analysis
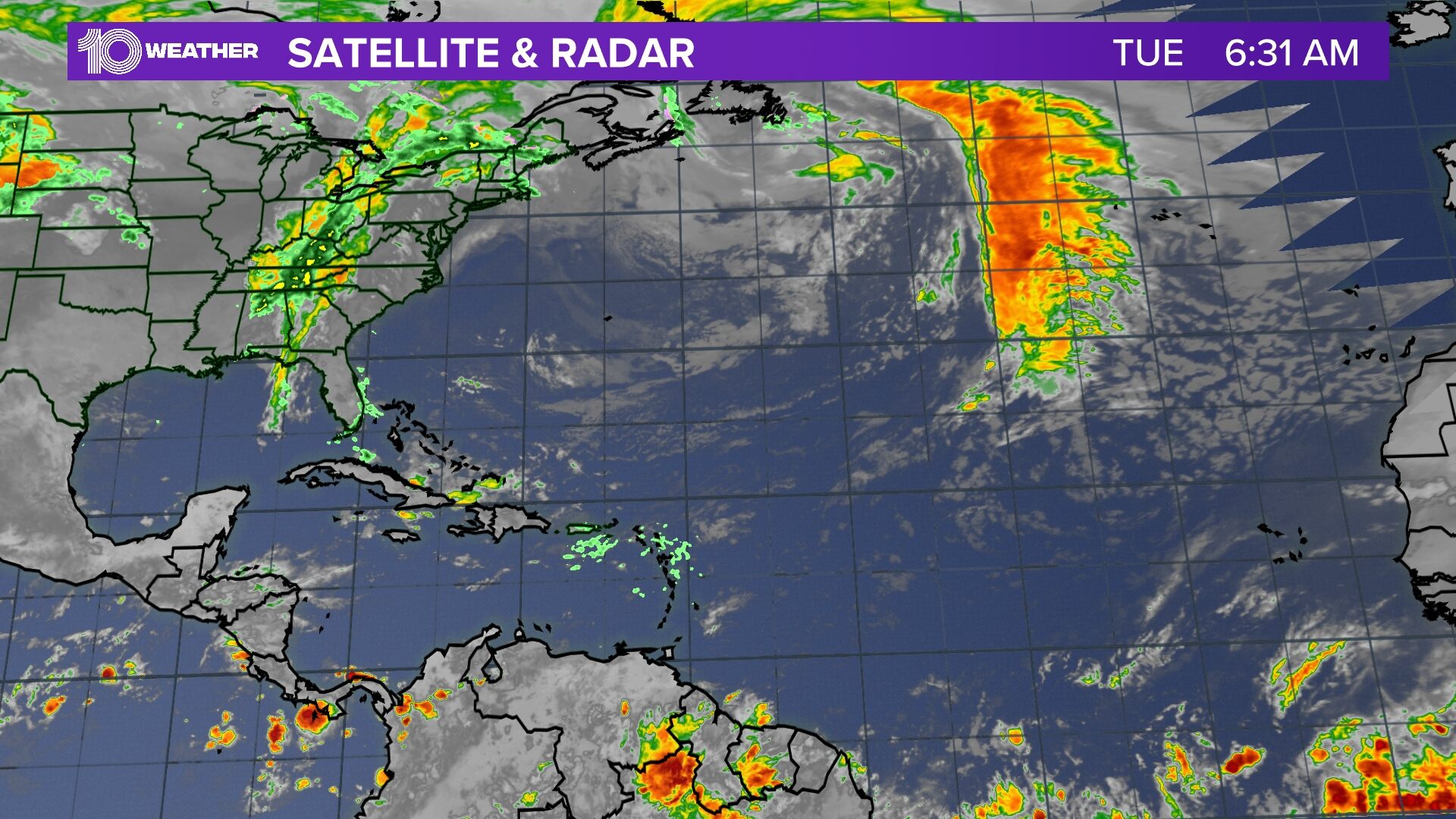
Hurricane Beryl, a Category 1 storm, is forecasted to move over the Atlantic Ocean and is anticipated to strengthen as it approaches the Caribbean Sea. The spaghetti models provide an ensemble of potential tracks and intensities for the storm, offering insights into its likely behavior and potential impacts.
Upon analyzing the spaghetti models, a few key trends and patterns emerge. The models generally agree on Beryl’s initial track, predicting a northwestward movement towards the Caribbean Sea. However, there is some divergence in the models’ predictions beyond this point. Some models suggest Beryl could make landfall in Central America, while others indicate it may continue on a more northerly track, potentially impacting the southeastern United States.
Potential Impacts and Implications
The potential impacts and implications of the spaghetti model predictions for Beryl vary depending on its ultimate track and intensity. If Beryl makes landfall in Central America, it could bring heavy rainfall, flooding, and potential landslides to the region. If it continues on a more northerly track, the storm could impact the southeastern United States, potentially bringing similar hazards to coastal areas and inland regions.
Given the uncertainty in the spaghetti model predictions, it is crucial to monitor the storm’s progress closely and follow official advisories from the National Hurricane Center. Residents in potentially affected areas should take necessary precautions and stay informed about the latest forecasts.
Model Comparison and Interpretation
Comparing spaghetti models with other forecasting models like the European and GFS models is crucial for a comprehensive understanding of hurricane behavior. While these models share the common goal of predicting storm paths, they differ in their underlying assumptions and methodologies.
Reasons for Discrepancies and Similarities, Hurricane beryl spaghetti models
- Data Sources and Resolution: Different models utilize varying data sources and resolutions, leading to discrepancies in initial conditions and subsequent forecasts.
- Physical Parameterizations: Models employ different mathematical equations to represent atmospheric processes, resulting in variations in storm simulations.
- Ensemble Size: Spaghetti models typically consist of multiple ensemble members, providing a range of possible outcomes, while other models may have fewer or no ensemble members.
Interpreting and Using Spaghetti Models
When using spaghetti models, it’s essential to consider their limitations and strengths. Spaghetti models:
- Illustrate Uncertainty: The spread of spaghetti lines represents the uncertainty in the storm’s path and intensity.
- Provide Probabilistic Forecasts: The density of spaghetti lines in a particular area indicates the likelihood of the storm passing through that region.
- Complement Other Models: Spaghetti models should be used in conjunction with other forecasting tools, such as track and intensity forecasts, to enhance predictive accuracy.